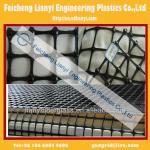
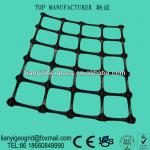
Biaxial geogrid for soil reinforcement of wall/steep slope/roadway base/foundation - HX-G02
| Type: Geogrids | Place of Origin: Hebei China (Mainland) | Brand Name: Hexing | Model Number: HX-G02 |
| Material: plastic,fiberglass,plastic-steel,polyester etc | Width:: 1-6m | Length:: as your reqiurement | Opening Size:: 12-50mm |
| Tensile Strength:: ≥25 -≥120KN/m | Elongation:: less than 4% | Type:: uniaxial,biaxial |

Biaxial geogrid
Introduction
A geogrid is defined as a grid structure of polymeric material formed by weaving or knitting intersecting ribs with appropriate apertures (opening sizes) to allow interlocking with surrounding soil, rock, earth and other surrounding materials. There are two basic categories of geogrids. Uniaxial geogrids designed to endure stress in one direction. Their main strength is in the machine direction making these grids suitable for wall and slope applications. Biaxial geogrids provide equal strengths in both machine and cross directions making them suitable for bases or foundation application where stresses can occur in any direction. Depending upon manufacturing techniques and materials, geogrids can be designed to resist creep when subjected to high loads for long periods of time or resist high, short-term dynamic loads or moderate loads over longer periods of time.
Material
plastic,fiberglass,plastic-steel,polyester etc
Specification
Example offiberglassgeogrid
Advantages
· Reduce costs- apertures designed to work with wide range of fill allowing for the use ofless expensive soils
· Reduce depth of excavation required on unsuitable sub grades
· Increase developable areas without incurring cost of unattractive and expensive retaining wall
· Stabilizing slopes increases the strength of soil giving it a higher factor of safety and greaterseismic durability
· Reduces maintenance and extends the life of the pavement by reducing differential settlementof roadways
· Durability – high resistance to soil micro-organisms and chemicals, UV radiation and mechanical damage
Applications
Geogrids focus almost entirely on reinforcement applications, although separation may be a function. The following are examples of a few applications.
· Slope Reinforcement- embankments over soft soils, extra-steep earthwork slopes, landfill liner systems, and industrial and contaminated land reclamation
· Base Reinforcement- foundations of roadbeds, parking lots, railroad tracks beds, airports runways, permanent unpaved roads, construction haul roads
· Wall Reinforcement- retaining walls, sea walls, airport noise barriers, and bridge supports
· Berm Reinforcement - spillway channels for earthen dams, levees, and waste contaminated ponds, banks for earthen canals and waterways
| Packaging Detail:standard export packing |
| Delivery Detail:10 days or as your requirement |